Contact
Email:
Alexandra.Bohne@lmu.de
Control and Regulation of Chloroplast Gene Expression by RNA Binding Proteins
Due to the endosymbiotic origin of chloroplasts, many of the proteins constituting the multisubunit complexes of the thylakoid membrane are nowadays encoded in the nucleus while others are encoded in the chloroplast itself. Chloroplast gene expression therefore needs to be coordinated with the nuclear one to allow a balanced assembly of protein complexes. In addition, gene expression of the organelle requires an adaption to a changing environment to meet the demand of the cell. Remarkably, the majority of proteins controlling chloroplast gene expression belongs to the superfamily of helical repeat proteins, primarily represented by PentatricoPeptide Repeat (PPRs), TetratricoPeptide Repeat (TPRs), and the more recently described OctotricoPeptide Repeat (OPRs) proteins. By posttranscriptional mechanisms, like the stabilization of the RNA or translation initiation helical repeat proteins determine steady state levels of plastid transcripts and their encoded proteins.
To date, the predominant role of OPRs as key players for the posttranscriptional control of chloroplast gene expression in the green algal model organism Chlamydomonas reinhardtii is just emerging. The RNA targets of the majority of these proteins as well as their molecular working modes are unknown. Moreover, the specific interaction of these helical repeat proteins with their plastid target RNAs makes them ideal candidates to promote an adaption of chloroplast gene expression to changing environmental conditions, in particular light. We therefore aim at elucidating mechanistic principles of regulation and adaption of chloroplast gene expression by OPR and PPR proteins and to identify new players involved in these processes.
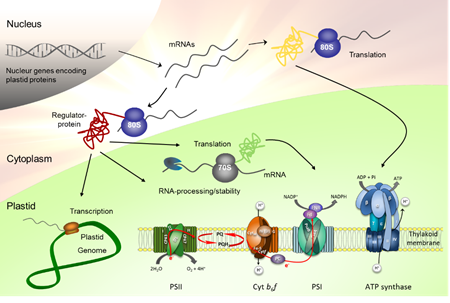
Fig. 1. Control of plastid gene expression by nucleus-encoded proteins. After their expression in the nucleus, RNAs encoding regulatory proteins are translated in the cytosol. The proteins are then imported into the organelle where they fulfil a variety of functions in chloroplast RNA metabolism.
For more information visit here.

